Jurisdictions Hub ❯ Singapore Singapore Verification & Risk Requirements

Overview
Singapore’s KYB landscape at a glance
Singapore KYB is high clarity via ACRA and UEN, but filings, ownership and ongoing updates still need review.
See Overview
Challenges
Why Singapore is difficult to verify
Singapore KYB is straightforward, but complex or cross-border structures complicate identity and risk checks.
Assess Challenges
Requirements
What you need for accurate KYB
Verified registry access, clear ownership visibility, structured translations, and AML signals.
Inspect Requirements
Resources
For Singapore-focused teams
Access data sources, verification standards, and tools that help teams complete KYB, UBO, and AML checks.
Access ResourcesOverview Singapore KYB Jurisdiction Overview
For KYB, Singapore is often regarded as a relatively “high clarity” jurisdiction, but verification still requires careful review of filings, ownership/control data, and ongoing updates (e.g., directorship changes, charges, and regulatory or enforcement signals).
This jurisdiction profile summarises the main factual aspects relevant to understanding corporate information in Singapore.

Challenges When Verifying Companies In Singapore
compliance teams still encounter common challenges when confirming identity, control, and risk indicators, particularly with complex structures or cross-border onboarding.

Different Entity Types and Status
Singapore has multiple entity types and registration statuses. Verification requires confirming the correct structure and current status in official records.
Control and Beneficial Ownership
Companies must maintain a Register of Controllers, but beneficial ownership is not always fully visible in standard public registry extracts, particularly where ownership structures are layered.

Timeliness of Changes and Monitoring
Company details such as directors, ownership, business activities, and status can change over time. Updates may not always appear immediately across public records, making ongoing monitoring important.

Interpreting Corporate Filings
Registry data provides key information, but filings still require interpretation to distinguish current status, historical changes, and disclosures that may need further verification.
Connected Entities and Group Structures
Group structures, holding entities, and cross-border links can obscure ownership and control, often requiring analysis beyond a single registry record.

Risk Signals Beyond The Registry
Some risk indicators sit outside basic registry data, such as enforcement actions, adverse media, or sanctions information, and may require additional screening beyond standard filings.
Requirements For Singapore KYB
Essential Identifiers for Companies in Singapore
Singapore uses a standardised set of identifiers to match companies to official registry records.
Unique Entity Number (UEN)
Singapore’s universal business identifier is issued to every registered entity. The UEN is the primary reference used across government systems to identify and track companies.
Registered Entity Name
The entity’s legal name as registered with the Accounting and Corporate Regulatory Authority (ACRA). This is the authoritative reference used for record matching and verification.
Entity Type & Registration Status
Singapore supports multiple entity types, including companies, partnerships, branches, and representative offices. Verifying the correct entity type and current registration status is essential for accurate KYB.
Registered Address
Each entity maintains a registered business address on file with ACRA, which forms part of its official registry record.
Common Public Documents Available in Singapore
Singapore publishes a range of standard corporate information through its national registry, though availability may vary by entity type.
Business Profile
The primary registry extract issued by ACRA. It includes the UEN, registered name, entity type, status, registered address, directors, shareholders (as disclosed), and principal activities.
Annual Filings
Companies are required to file annual returns and financial information. These filings confirm that an entity remains active and compliant with ongoing regulatory obligations.
Shareholder & Director Information
Public disclosures provide visibility into appointed directors and registered shareholders, subject to statutory disclosure thresholds.
Historical Filing Records
Registry extracts may reflect historical changes to directors, addresses, entity status, or business activities over time.
Official Sources of Corporate Information
Corporate information in Singapore is published and maintained by national authorities and relevant regulators.
ACRA (Accounting and Corporate Regulatory
Authority)
Singapore’s central business registry provides
official company records, filings, and
registration data.
Sector Regulators
Certain industries (e.g. financial services,
payment services, capital markets) are
overseen by additional regulators such as the
Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS), which
publishes supplementary licensing and
compliance information.
Judicial & Enforcement Databases
Separate public systems provide access to
court records, enforcement actions, and, where
applicable, insolvency or winding-up
proceedings.
Resources Compliance insights, explained
Singapore strengthens AML framework. How does this impact your business?
Understand how Singapore’s updated AML framework changes onboarding and compliance obligations
Read MoreSolutions How AsiaVerify Supports KYB in Singapore
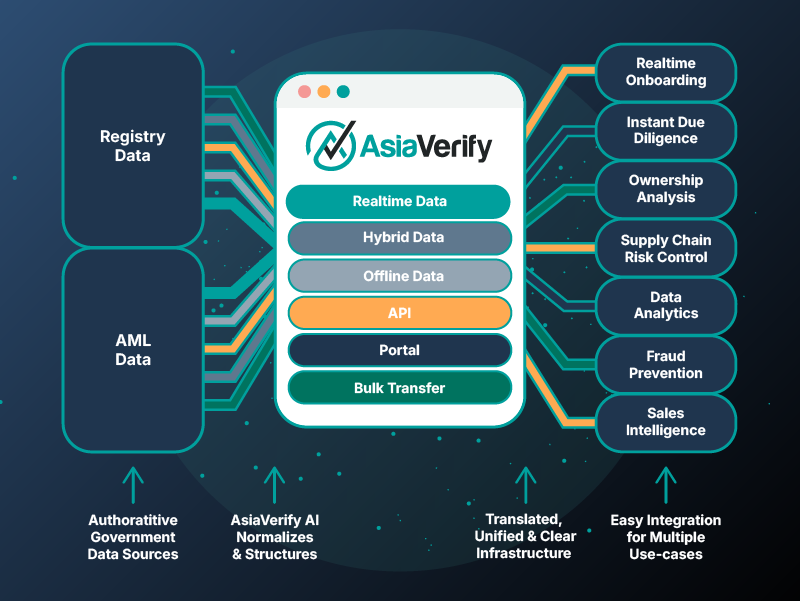
Real-time Registry Connection
AsiaVerify connects to authoritative sources to retrieve key company information and filing updates, helping teams validate entities using current, source-backed data.
Directors & Shareholders Data
Access structured data on key people and ownership where available, supporting clearer review of decision-critical relationships and changes over time.
Automated Document Retrieval
Retrieve supporting documents and filing records from official
sources, when available, to reduce back-and-forth and speed up evidence collection.
AI-assisted Translation & Normalisation
AsiaVerify uses AI to structure, normalise, and translate registry
data where required, aligning disparate inputs into a consistent, review-ready format for reliable KYB decisions..
UBO Mapping & Ownership Analysis
AsiaVerify reconstructs ownership layers using disclosed shareholder information and historical filings, helping teams identify controlling individuals and entities even in complex, multi-tier structures.
AML & Sanctions Screening
Entities, shareholders and legal representatives are screened against sanctions, enforcement lists and adverse media to support AML and CTF obligations across APAC.
API, Portal and Bulk Access
Teams can integrate real-time verification through API, run checks on-demand in the portal, or process high volumes via bulk upload — ensuring KYB workflows match operational needs.
Ongoing monitoring & alerts
AsiaVerify continuously monitors changes to business status, registered details, shareholders, scope, and penalties, alerting teams when regulatory or structural changes occur.
From Sydney to Shanghai APAC Coverage You Can Trust